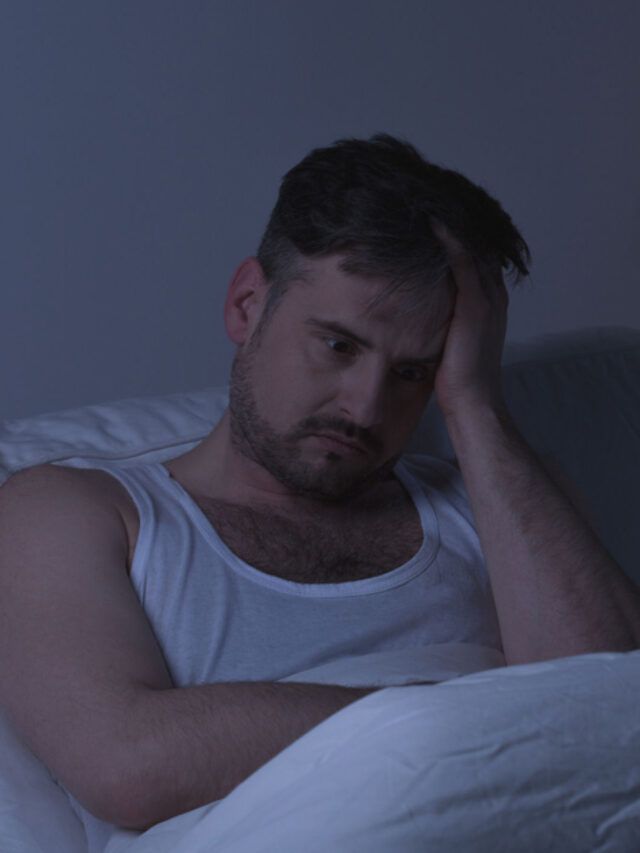
A good night’s sleep is a precious commodity, yet for many women, the persistent need to urinate during the night, known as “nocturia,” becomes a disruptive challenge. A recent study published in The Journal of Urology revealed that up to 44% of women aged 20 to 40 experience this condition, significantly more than men. In this article, we delve into the causes, signs, symptoms, and treatment options for nocturia, shedding light on a prevalent yet often overlooked aspect of women’s health.

Understanding Nocturia:
Nocturia is characterized by the frequent need to urinate during the night, leading to interrupted sleep patterns. Women, particularly those aged between 20 and 40, are disproportionately affected, with up to 44% experiencing nightly disruptions.
Causes of Nocturia:
Several factors contribute to the development of nocturia, ranging from lifestyle choices to underlying medical conditions. Common causes include drinking fluids before bedtime, alcohol or caffeine consumption close to sleep, smoking, certain medications, and various health conditions such as diabetes, urinary tract infections, kidney disease, and bladder problems. Age, hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause, and conditions like sleep apnea also play a role.
Signs and Symptoms:
Nocturia manifests through various signs and symptoms, including an increased need to urinate during the day, difficulty in urination, a weak urine flow, pain or blood in the urine, mood changes or irritability due to lack of sleep, and incontinence or urine leakage. Recognizing these indicators is crucial for seeking timely medical intervention.

Risk Factors:
David Shusterman emphasizes that age, weight, race, and gender influence the likelihood of developing nocturia. Acknowledging these risk factors allows for a more comprehensive understanding of individual susceptibility to this condition.

Treatment Approaches:
Managing nocturia involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and targeted medications tailored to address the underlying causes. Treatment strategies vary based on the root cause, with examples including medications or procedures to shrink an enlarged prostate, diabetes management for those with diabetes-related nocturia, and oral medications for individuals experiencing bladder issues.
Consequences of Untreated Nocturia:
Neglecting to seek medical attention for nocturia can lead to various health complications. Daytime fatigue, mobility issues, mental health problems, and an increased risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the potential consequences. Recognizing and addressing nocturia is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Conclusion:
Nocturia is a prevalent yet often underestimated condition, significantly impacting women’s sleep quality. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can regain control over their nighttime routine and mitigate potential health risks associated with untreated nocturia.






